Fossil resources leave a significant carbon footprint for plastic products. By 2050, plastics could make up 20 % of global oil and gas consumption and account for 2.8 gigatons of GHG emissions per year*. It is clear that when striving to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the use of fossil resources in plastics must be reduced significantly.
*CIEL: Plastic & Climate: The Hidden Costs of a Plastic Planet, 2019
Renewable and recycled plastics
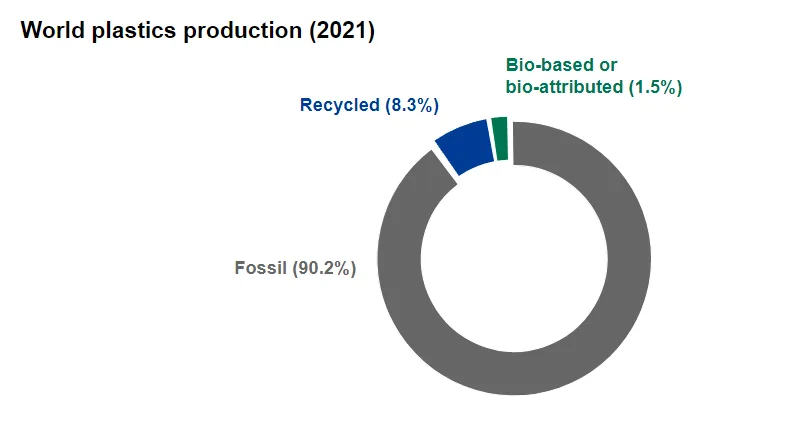
At the same time, a vast majority of plastic waste worldwide is not being recycled. Most of it ends up incinerated, in landfills or – in the worst case scenario – in the environment.
In fact, less than 10 percent of plastic waste gets recycled**. This is not only a waste of resources, but mismanagement and landfilling of plastic waste also lead to significant environmental damages.
Products and innovation
Global GHG emissions from plastics production & incineration
1.3 GT
2030
2.8 GT
2050
Plastics are prominently associated with these two issues. In fact, the negative impacts often overshadow the positive properties of the material: the numerous applications that rely on plastics and their benefits.
Reducing the use of plastics may be a valid concept for some applications—and it should be a priority in solving the plastics dilemma—but it won’t be the solution for all applications. The same is true for reusing plastics: from a climate impact and resource efficiency point of view, wherever plastics is used, they always should be reused.
In addition to reducing and reusing plastics, the replacement of fossil materials in plastics and a significant transition from incineration and landfilling of plastics to recycling should be prioritized. This approach not only minimizes waste but also contributes to a more sustainable plastics economy.

Products and innovation
A solution: Neste RE™
Our approach to enabling the plastics industry's transition away from fossil is simple: change the source of the carbon, do not change the product. Neste RE™ is a raw material for the production of plastics that can replace fossil raw materials for steam crackers.
Read more about Neste REReleases and news
Here you will find our latest press releases and news on renewable plastics and circular economy.
Contact Neste
*The New Plastics Economy: Rethinking the future of plastics, World Economic Forum, 2016 ; Plastics and Climate: the hidden cost of a plastic planet, Center for International Environmental Law, 2019 **Global Plastics Outlook World, OEC, 2022